
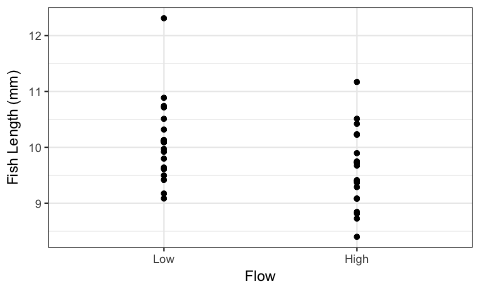
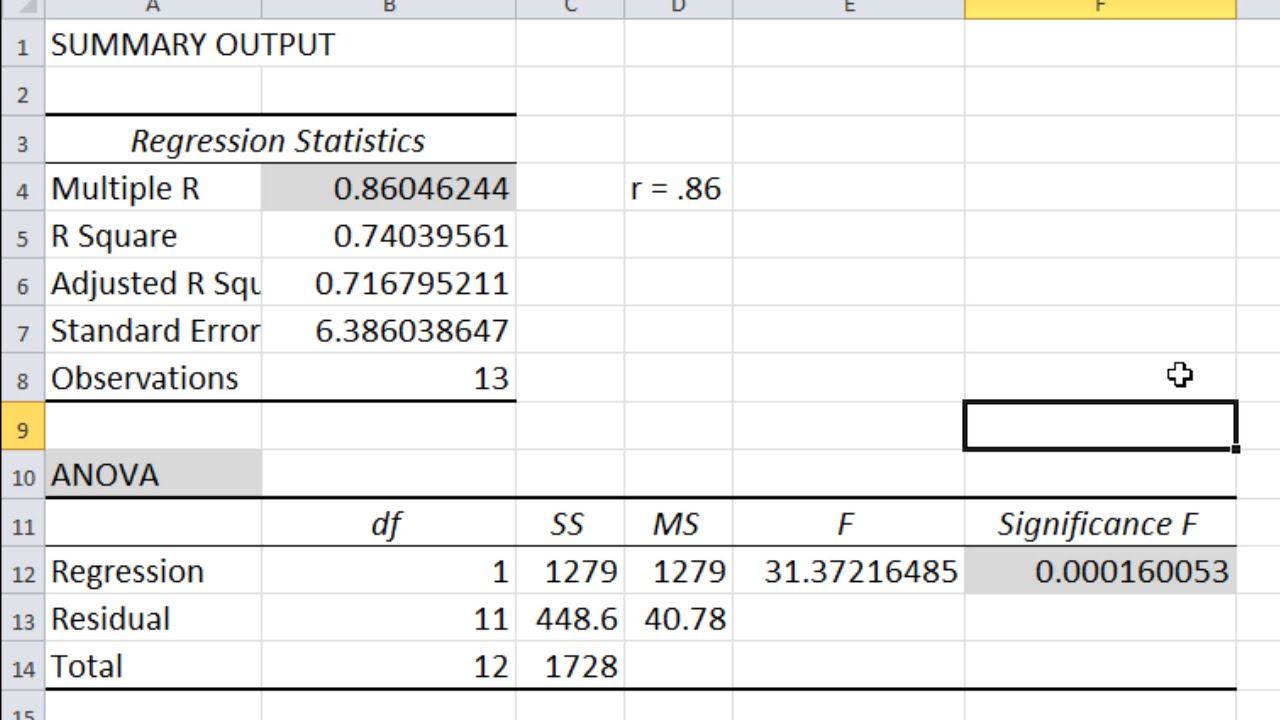
In your particular case this is an odd calculation, since the observed test statistic is above the mode of the null density, but its left-tail is the smaller probability. In the case of a left-tailed case, the critical value corresponds to the point on. To implement this method for the two-sided variance test, let $\text^2 | H_0) \Big).$$ Compute critical F values for the F-distribution using the form below. This calculator will tell you the probability value of an F-test, given the F-value, numerator degrees of freedom, and denominator degrees of freedom.
Free p value calculator f test free#
With an asymmetric null distribution, this leads you to a p-value calculated with unequal tails. Free p-Value Calculator for an F-Test p-Value Calculator for an F-Test. Under this method, the p-value is the probability of falling in the "lowest density region", where the density cut-off is the density at the observed test statistic. Value from F-Ratio Calculator (ANOVA) This should be self-explanatory, but just in case it's not: your F -ratio value goes in the F -ratio value box, you stick your degrees of freedom for the numerator (between-treatments) in the DF - numerator box, your degrees of freedom for the denominator (within-treatments) in the DF - denominator box, select your significance level, then press the 'Calculate' button. This is the interpretation used in a standard likelihood-ratio (LR) test. To perform Fisher’s Exact Test, simply fill in the cells of the. It is typically used as an alternative to the Chi-Square Test of Independence when one or more of the cell counts in a 2×2 table is less than 5. Lowest-density p-value calculation: The most sensible thing method of two-sided hypothesis testing is to interpret "more extreme" as meaning a lower value of the null density. Fisher’s Exact Test is used to determine whether or not there is a significant association between two categorical variables. Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F. Because this test has an asymmetric null distribution, we need to specify exactly what we mean by "extreme". Determine your GFR value using the GFR Calculator to help measure kidney function. The p-value is the total area under the null density for all values in the lower and upper tails of that density that are at least as "extreme" (i.e., at least as conducive to the alternative hypothesis) as the observed test statistic. What you are dealing with in this question is a two-sided variance test, which is a specific case of a two-sided test with an asymmetric null distribution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
